There is no other option for efficiency, precision, and design accuracy when talking about modern engineering and the product development landscape.
SolidWorks is one of the leading CAD platforms. It is trusted by 6 million+ engineers worldwide. It enables 3D modelling, simulation, and assembly design.
One of its most powerful capabilities is Assembly Modeling. Here, designers bring individual parts together to form complete mechanical systems. To master this assembly design, it is a must for the engineers to understand two foundational modelling approaches, i.e., Top-Down and Bottom-Up.
In this article, we will discuss SolidWorks, what it is, how it works, and many other things related to it.
What is Assembly Modeling in SolidWorks
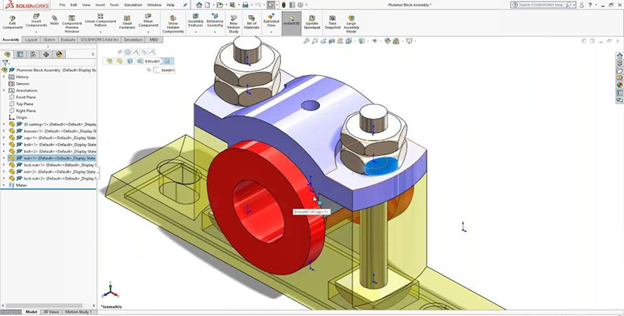
Assembly modelling involves organizing, orienting, and connecting 3D parts to build functional products.
It offers powerful tools for:
- Mates and constraints
- Motion simulation
- Interference Detection
- Design Configuration
- Real-time updates across the parts
According to the study by CIMdata, the companies using structured assembly modelling reduce the engineering rework by up to 45%. And it ensures faster design cycles and fewer production errors.
What are the Assembly Modelling Approaches
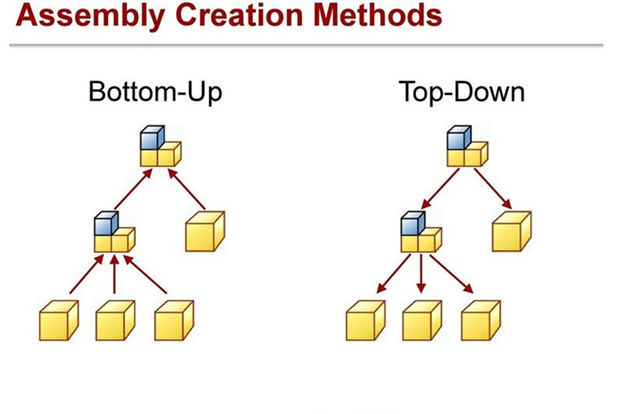
There are mainly two types of Assembly Modeling Approaches:
- Bottom-Up Assembly Modeling
- Top-Down Assembly Modeling
Bottom-Up Assembly Modeling
It is the traditional approach. Here, in this approach, each part is created independently before being inserted into the assembly environment.
How the Bottom-Up Approach Works
It involves three steps:
- Design all the individual parts separately.
- Insert them into the assembly workplace.
- Apply mates (such as concentric, parallel, or coincident) to position the parts accurately.
Advantages
- High reusability of parts across different projects.
- Ideal for designs with standardized components.
- Simple, structured workflow for beginners.
- Works well with vendor-supplied or purchased parts.
Limitations
- Time-consuming while dealing with complex interdependencies.
- Changes in one part often require manual updates in others.
- Greater risk of alignment or tolerance issues.
Where It’s Used
- Industrial machinery
- Consumer products with standardised components
- Assemblies where parts are predefined.
Top-Down Assembly Modelling
It is also known as the master model. It is the modern approach. Here, the design process begins at the assembly level. Parts are created in context, meaning they reference each other for size, position, and shape.
How It Works
- Start with the empty assembly
- Create layout sketches or reference geometry.
- Build individual parts inside the assembly environment.
- Allow relationships to update automatically.
Advantages
- Fast and highly efficient for complex designs.
- Automatically updates linked components when changes are made.
- Ideal for motion-based systems and multi-body designs.
- Reduces rework and improves accuracy.
Limitations
- It requires careful planning to avoid messy reference links.
- It will be challenging for the large teams without naming the conventions.
- It is unsuitable for using the purchased components.
Where it’s used
It is used in:
- Robotics
- Aerospace systems
- Automotive Assemblies
- Mechanism for heavy products
How to Select the Best Approach: Top Down vs Bottom Up
| Criteria | Bottom-Up Approach | Top-Down Approach |
| Reusability | High | Medium |
| Change Propagation | Manual | Automatic |
| Workflow Complexity | Simple | Advanced |
| Best For | Standardised Design | Complex Integrated Systems |
Most of the experienced engineers use the hybrid approach. As it helps them to grab the structure of Bottom-Up and the efficiency of the Top-Down approach for the best results to achieve.
Why Learning These Approaches Boosts Your Career
- High hiring priority across industries.
SolidWorks skills have become a hiring priority across industries.
It is reported by The American Society of Mechanical Engineers (ASME) that 89% of engineering job postings mention SolidWorks as a required or preferred skill, and the certified professional enjoys higher salary potential.
- Enrolling in the SolidWorks online classes with a certificate in this online training course helps you to build:
- Hands-on assembly design mastery
- Understanding of mates, constraints, and motion links
- Real-world industry projects
- Strong technical portfolio
The certifications help you to validate your expertise, making you more attractive to employers in manufacturing, automotive, aerospace, product design, and engineering services.
Conclusion
Mastering the Top-Down and Bottom-Up approach of the assembly modelling helps you with the ability to design smarter, faster, and with great accuracy.
As with the development in every field, engineering becomes more competitive. And structured learning through the certified online training helps you to become industry-ready.
Ready to master professional assembly modelling?
Begin your SolidWorks online certification course today and transform your design career with hands-on, structured learning.
Contact us today to get started!